Eustachian tube dysfunction
Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is defined as the ear's inability to appropriately equalize pressure. ETD can lead to chronic ear pressure, pain or discomfort with pressure changes.1
Typically, when you yawn, sneeze, or swallow, your eustachian tubes- small passageways that run between your middle ear and upper throat- open to keep pressure and fluid from building up. When these eustachian tubes are blocked, this is when you might feel a fullness in your ear or your hearing may be muffled.1
CAUSES
Eustachian tube dysfunction can be caused by:2
- colds
- flus
- sinus infections
- allergies
- altitude changes cause by activities such has hiking, flying on a plane, or even riding an elevator
SYMPTOMS
There are numerous symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction, but you should consult with your doctor for diagnosis. Typical symptoms include:2
- Plugged or full feeling in the ears
- Pain in one or both ears
- Sounds seem muffled
- Ringing in one or both ears
- Popping, clicking, or tickling sensation in the ear
- Balance problems

TREATMENT
There are an estimated 11 million adults suffering from Eustachian tube dysfunction in the US and over 2 million healthcare visits every year.3 Treatment options range from medical management to invasive surgical options.2,4
Treatment options
If your symptoms persist, your doctor may recommend the following treatment options:
- Temporary relief: You can take certain actions to open up the tubes, such as swallowing, yawning, or chewing gum.4
- Valsalva maneuver: This maneuver can be done at home by taking a deep breath, pinching your nostrils closed, and blowing with your mouth shut.4
- Over-the-counter treatments: Decongestants to reduce the swelling of the lining of the tubes; Antihistamines and/or steroid nasal spray to reduce an allergic response4
- Medication: If a bacterial infection is present, your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic.4
Surgical treatments for Eustachian tube dysfunction
Some ETD sufferers with more severe or chronic symptoms may require surgical intervention. Consult with your physician to determine if one of the following may be the correct course of treatment:
- Fluid removal: After making a tiny incision in the eardrum, your doctor can suction out fluid from the middle ear, giving the Eustachian tube lining time to shrink while the eardrum is healing.5
- Ear tubes: Implantation of small tubes in the eardrums allows built-up fluid to drain out of the middle ear. This procedure is commonly performed on young children who get frequent ear infections. The tubes stay in for up to 18 months and fall out on their own.5
- Balloon dilation: Balloon dilation of the eustachian tube reduces local inflammation and/or hypertrophic mucosa volume though compression or crushing of the mucosa.5
Eustachian tube balloon dilation for treament
Many of the current treatment options for Eustachian tube dysfunction are limited or invasive, but a newer, minimally invasive treatment option using balloon dilation can restore Eustachian tube function and relieve symptoms. The dilation systems have been shown in studies to provide a safe and effective treatment option for people with Eustachian tube dysfunction.8 During this procedure, your doctor will insert a small balloon through your nose and into your eustachian tube. The balloon will then be inflated for 2 minutes and then removed. This procedure can be done in the office, ambulatory surgery center (ASC), or hospital.

WHAT TO EXPECT WITH TREATMENT
What to expect during treatment?
First, in both the office, ASC and hospital procedures, your doctor will anesthetize the inside of your nose to ensure comfort during the procedure. Next, the doctor will guide the balloon device into your Eustachian tube. Once inside the Eustachian tube, your doctor will advance the balloon into the opening and expand it for 2 minutes. The doctor will then deflate the balloon and remove it from your nose.
What to expect after treatment?
Your doctor may recommend that you avoid blowing your nose or Valsalva maneuvers (taking a deep breath, pinching your nostrils closed, and blowing with your mouth shut)

FAQ
People who have gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, rhinosinusitis, and recent upper respiratory tract infections are at an increased risk of developing ETD.2
Allergies can also increase a person’s risk, as they can lead to frequent episodes of mucus production and congestion.2
Activities that can trigger symptoms include:2
- Hiking at high altitudes
- Skiing or snowboarding
- Scuba diving
- Flying
The most common side effects associated with balloon dilation of the Eustachian tube include: pain, tissue inflammation, damage to the Eustachian Tube and continued or worsening symptoms. Potential severe risks include: subcutaneous emphysema and carotid artery damage.6
Data has shown that 89% of patients were satisfied with the procedure at the one-year follow-up and 83% at the long-term follow-up (29 months).8
Your doctor will ask you to complete a survey to understand your symptoms and allergy history. Your doctor will also do an examination of your ear canals and sinuses to check for inflammation and mucus build-up.
If symptoms linger, recur, or get worse, your doctor may want to check for underlying problems or other conditions that could be leading to your symptoms. Tests may include:
- Valsalva maneuver: Pinching the nose and closing the mouth and trying to breathe out through the nose can sometimes help clear the ears if your symptoms stem from air pressure changes.
- Audiogram: During this test that measures your hearing, you’ll listen to sounds transmitted by an audiologist and press a button to signal when you hear something.
- Tympanogram: This test for pressure behind the eardrum is performed by inserting a tympanometer probe in the ear canal. The instrument changes pressure in the ear, generates a pure tone, and measures the eardrum responses to the sound at different pressures.
- Otoscopy/Nasopharyngoscopy: This involves insertion of a small, flexible camera into the ear or nasal passage, so the doctor can see the openings of the Eustachian tubes.
- CT scan: Specialized forms of X-rays can offer a detailed look at the bones involved in hearing.

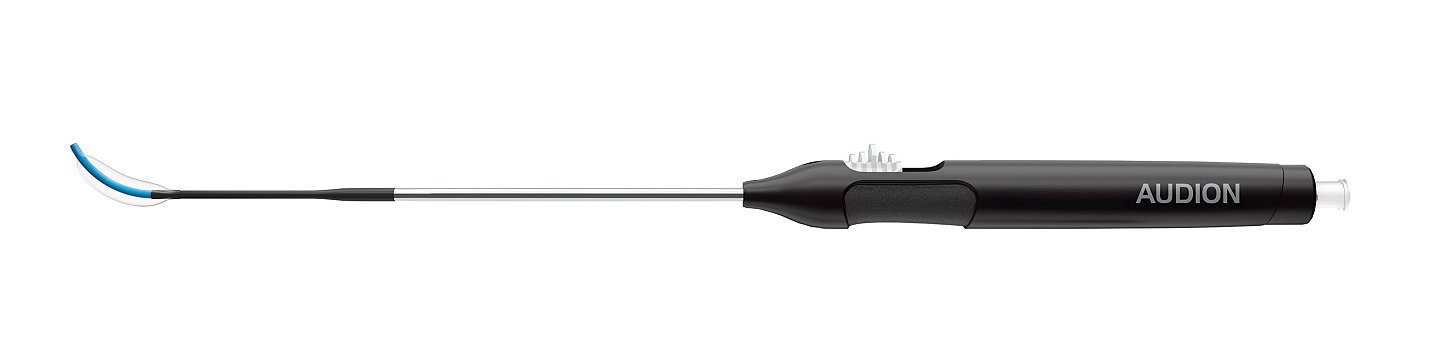
Audion® ET dilation system
The Audion ET dilation system is a balloon dilation device specifically designed for the Eustachian tube to treat adults (18+) with eustachian tube dysfunction. It features an atraumatic tip with an enhanced flexible design, 45 degree angle, and 20mm leg length designed to avoid critical anatomy.6, 10-11
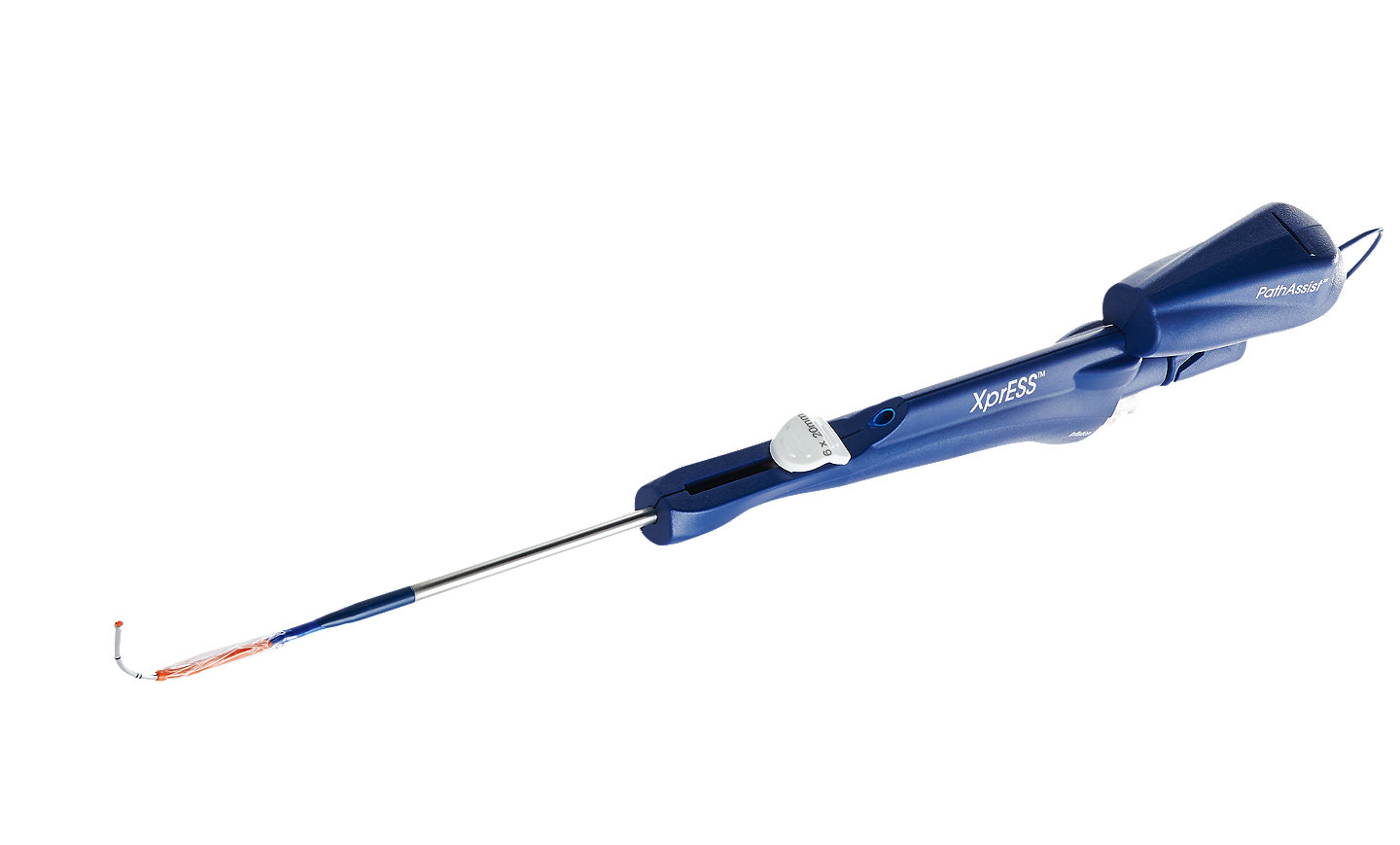

XprESS® ENT dilation system
This system delivers control and versatility for balloon dilation. Its seeker-based design and tip malleability provide the tactile feel and flexibility to address complex anatomy for a broad range of patients.7,9
References
- Schilder AG, Bhutta MF, Butler CC, Holy C, Levine LH, Kvaerner KJ, Norman G, Pennings RJ, Poe D, Silvola JT, Sudhoff H, Lund VJ. Eustachian tube dysfunction: consensus statement on definition, types, clinical presentation and diagnosis. Clin Otolaryngol. 2015 Oct;40(5):407-11. doi: 10.1111/coa.12475. PMID: 26347263; PMCID: PMC4600223
- Hamrang-Yousefi S, Ng J, Andaloro C. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. [Updated 2023 Feb 13]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555908/
- Shan A, Ward BK, Goman AM, Betz JF, Reed NS, Poe DS, Nieman CL. Prevalence of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction in Adults in the United States. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Oct 1;145(10):974-975. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2019.1917. PMID: 31369057; PMCID: PMC6681559.
- Llewellyn A, Norman G, Harden M, et al. Interventions for adult Eustachian tube dysfunction: a systematic review. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2014 Jul. (Health Technology Assessment, No. 18.46.) Chapter 1, Background. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK262265/
- “Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Definition, Symptoms & Treatment.” Cleveland Clinic, 17 Mar. 2022, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22527-eustachian-tube-dysfunction
- Audion instructions for use 5325-001
- XprESS instructions for use 4322-001
- Cutler, J. L., Meyer, T. A., Nguyen, S. A., O'Malley, E. M., Thackeray, L., & Slater, P. W. (2019). Long-term Outcomes of Balloon Dilation for Persistent Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. Otology & neurotology : official publication of the American Otological Society, American Neurotology Society [and] European Academy of Otology and Neurotology, 40(10), 1322–1325. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000002396
- Data on file at Stryker DHF 1656-001
- Data on file at Stryker DHF-2267-001
- Data on file at Stryker DHF-2265-001
ENT-GSNPS-SYK-662203
