SONOPET
Ultrasonic Aspirator
SONOPET Ultrasonic Aspirator delivers optimal flexibility for you, your team and your patients. It’s precise, easy to use and remarkably versatile. In one high-performance surgical aspirator, you get unparalleled control in soft-tissue applications—plus the nuanced power you need for fine bone dissection. Regulate ultrasonic power, suction and irrigation easily from the console.
We’ve designed every component of the SONOPET system for maximum performance, reliability and ease of use.
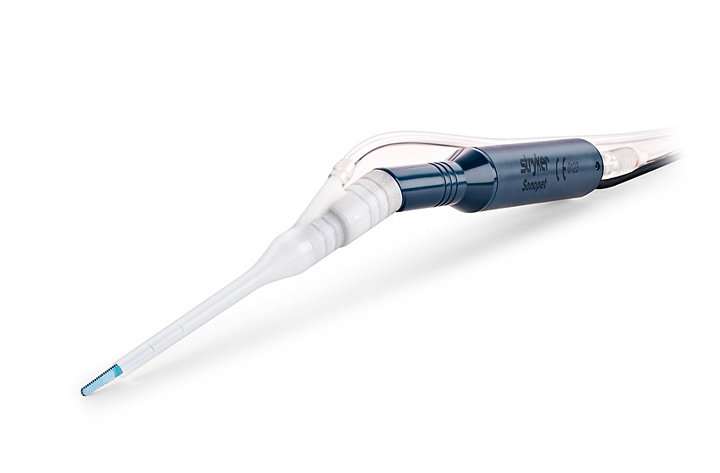
SONOPET
Proprietary LT vibration technology
SONOPET Ultrasonic Aspirator masters fine bone and hard tissue dissection by coupling longitudinal vibration with torsional oscillation. This patented innovation and ergonomic design let you emulsify bone with a high level of precision.
Because calcified and rigid structures don’t absorb ultrasonic oscillation, the SONOPET system cuts bone cells smoothly and efficiently. Underlying soft tissue vibrates with oscillation, moves away from the vibrating tip and remains largely unaffected.
Our bone tips gives you a high degree of control with minimal pressure. Helical reliefs machined into the shaft of the tip redirect the ultrasonic pulse from a purely longitudinal to longitudinal/torsional excursion.

Torsional oscillation

Longitudinal vibration
Versatile tips
Our superlong lengths give you access to deeper structures and are especially useful in applications that require minimally invasive approaches.
- Large selection of tips includes nine soft tissue tips and 11 bone tips
- Standard and superlong lengths allow for access into a variety of depths
- Available in a variety of diameters and lengths
- Detachable frangible sections allow for adjustable surface exposure

SONOPET console
When seconds matter, the efficiency and ease of the SONOPET system shine through. Because setup is quick and simple, you and your team can focus on what matters most—your patient.
- Durable, reliable standalone system with onboard suction and irrigation
- Non-sequential setup process for enhanced speed and efficiency
- Automatic handpiece recognition
- Precise control of ultrasonic power, suction and irrigation
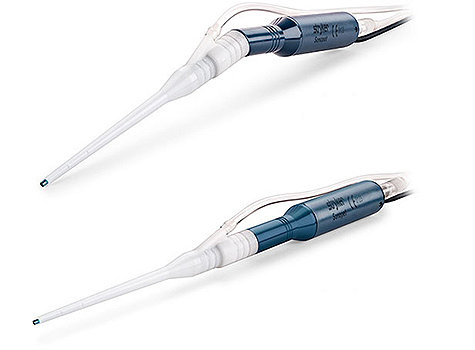
- Accept tips for soft tissue and bone
- Angled and straight models
- Tailored to surgeon preference, procedure and line-of-sight demands
- Lightweight, ergonomic design
- Superb tactile feedback, increased dexterity and less muscle fatigue
- Continuous irrigation and active suction keeps field clear of liquid and debris
- No external cooling required
- Frangible tip covers for better access and sightlines

Higher-frequency 34Hz angled handpiece
Designed for delicate tissue removal in superficial lesions, our 34kHz angled handpiece gives you enhanced tactile feedback and more nuanced control.
Higher frequency results in lower amplitude—the distance the tip moves along its length. Because lower amplitude delivers more selectivity and precision, this high-performance handpiece is ideal for work near critical structures and motor centers.